Material & Mechanical Tests
BASEC conducts a number of tests on cable materials. These tests are specified in cable and material standards and are called up for a variety of cable types.
Navigate Material & Mechanical Tests
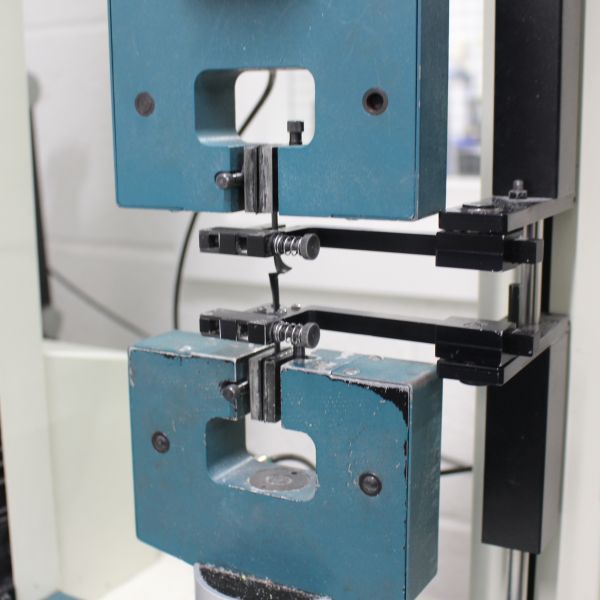
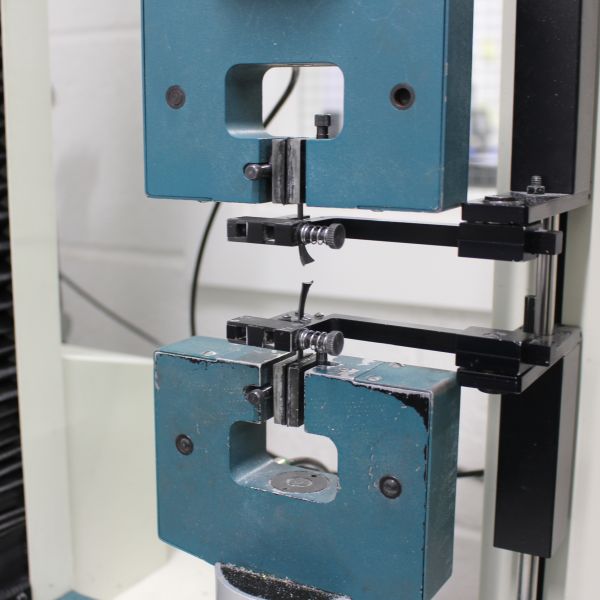
Tensile Strength and Elongation
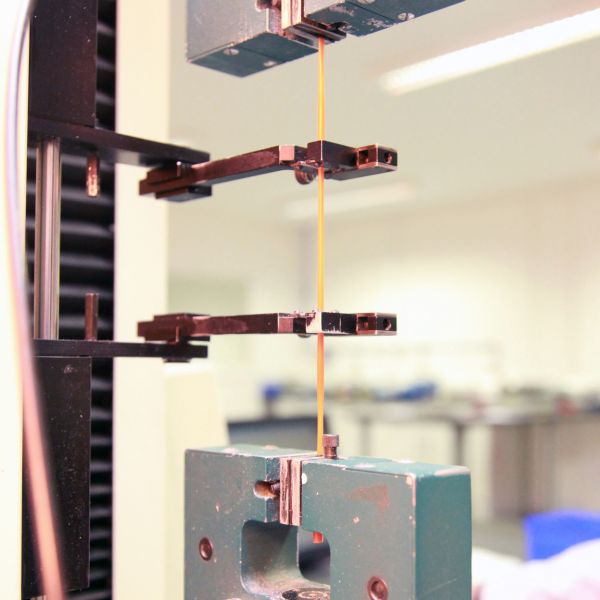
The tensile strength and elongation at break testing are used to assess the suitability of cable insulating and sheathing materials. Testing is not only conducted on samples of materials as manufactured but also after having elevated temperature conditioning to simulate several years of usage.
Example Cables

Nearly all cable types will have tensile strength and elongation at break testing conducted.
Test Methods & Equipment
Air oven, universal material testing machine & dimensional measurement equipment. The BS 7655 & BS EN 50363 series’ specifications detail the materials' acceptance criteria. The test methods are specified in BS EN (IEC) 60811-401 & BS EN (IEC) 60811-501.
Tensile strength of aluminium armour wires
Cold Bend / Cold Impact
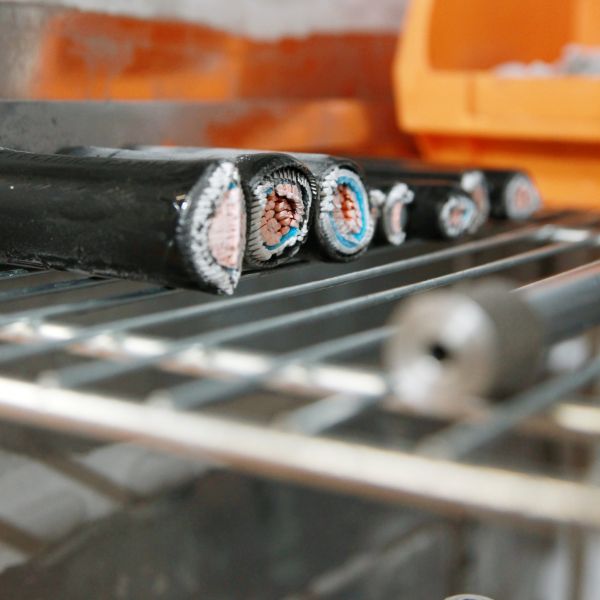

Tests to check that cables can withstand bending/elongation and impact at low temperatures to ensure that the materials do not crack during installation and normal use.
Example Cables

These cold tests are intended for sheathed cables of any type, irrespective of the type of insulation of the cores, and for the insulation of wires, cables and flat cables without sheath.
Test Methods & Equipment
Freezer, test mandrels & impact device. The test methods are specified in BS EN (IEC) 60811-504, BS EN (IEC) 60811-505 & BS EN (IEC) 60811-506.
Hot Set
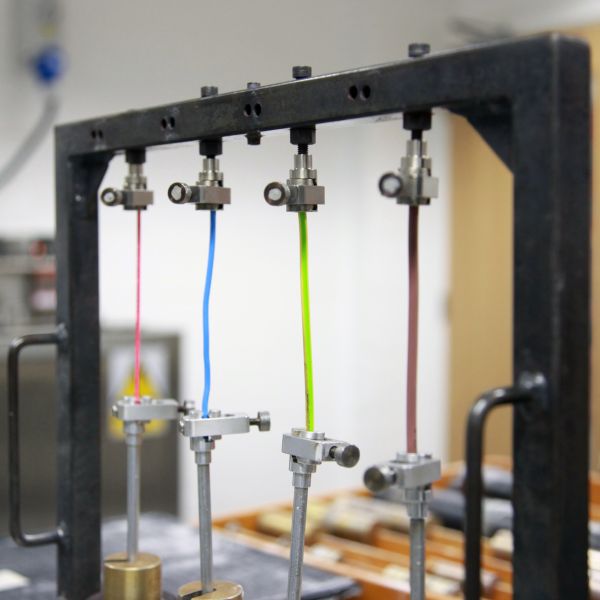

The hot set test is used to check that there is sufficient cross linking within a material.
Example Cables

Typically applies to cross-linkable compounds used for insulating and sheathing.
Test Methods & Equipment
Oven, loaded test grips & dimensional measurement equipment. The test method is specified in BS EN (IEC) 60811-507.
Hot Pressure
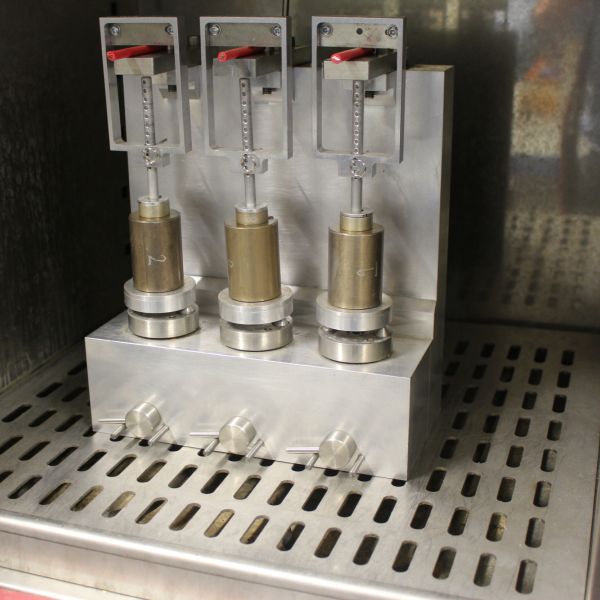

The pressure test at high temperature is used to check that sheathing and insulation materials are resistant to indentation at elevated temperatures.
Example Cables

Typically applies to cables with thermoplastic insulating and sheathing compounds.
Abrasion
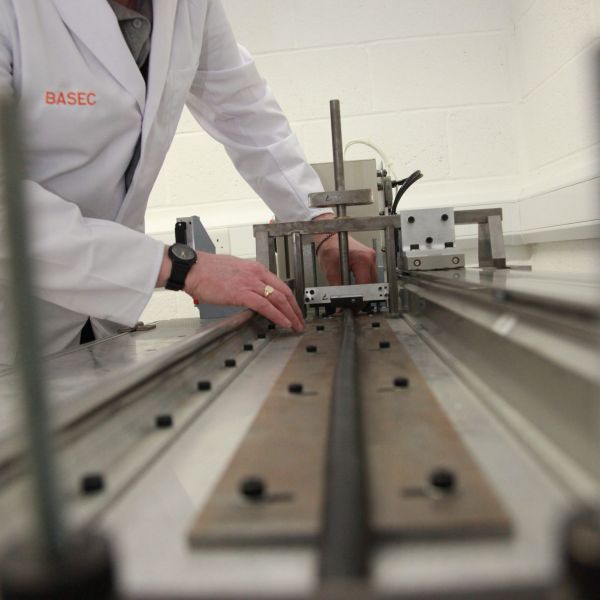

The purpose of this test is to demonstrate that an extruded oversheath will withstand abrasion during the laying operation.
Example Cables

Some examples of the types of cables that subjected to this test:
Test Methods & Equipment
A steel angle vertically loaded above the point of contact with the cable is moved repeatedly along a length of cable in accordance with BS EN 60229.
Tear Test
Shrinkage
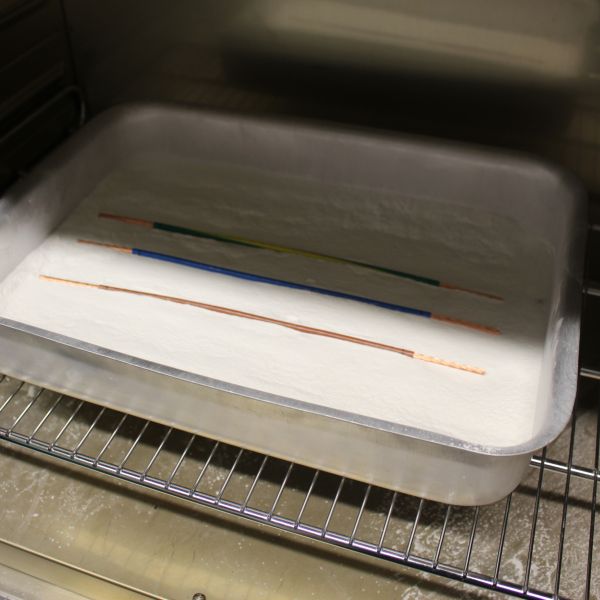

This test determines the amount of shrinkage of the insulation/oversheath during exposure to heating. If the amount of shrinkage is excessive, this could lead to conductors being exposed during normal usage.
Example Cables

Examples of the types of cables that subjected to this test:
Test Methods & Equipment
Steel rule and electrically heated oven using the methods described in the cable standards and BS EN (IEC) 60811-502.

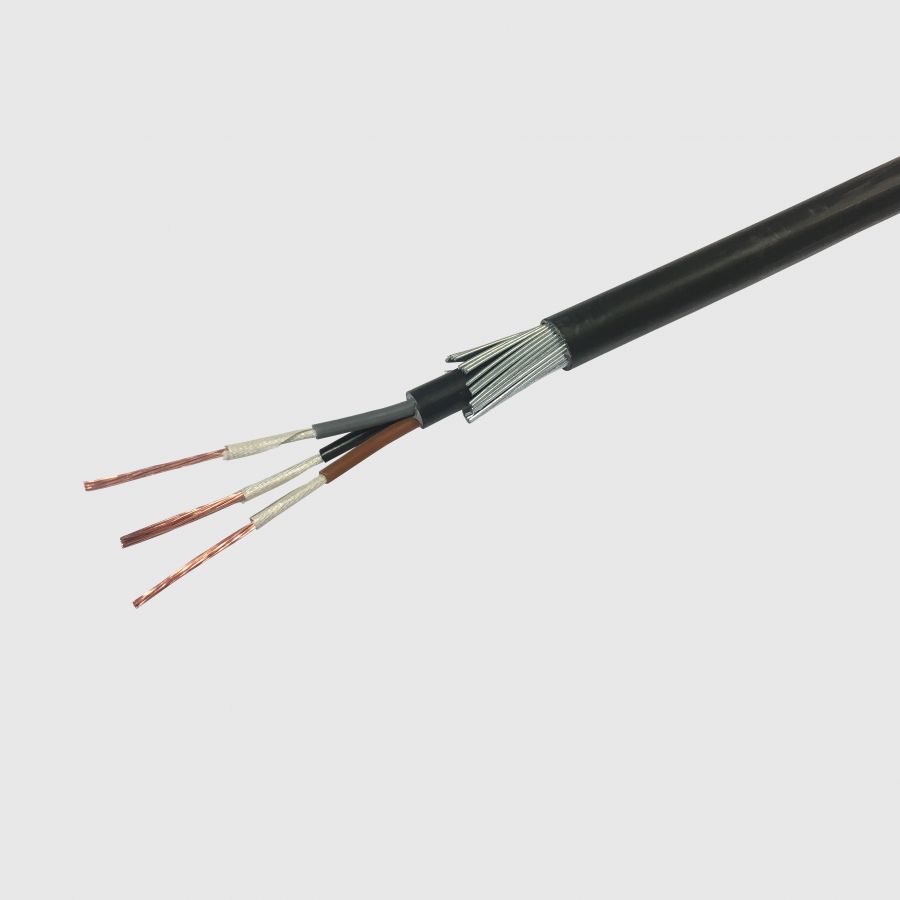
BS 5467
Armoured power cables with PVC sheathing. Commonly known as PVC sheathed armoured, SWA, AWA.

BS 5839-1
Alarm system design standard which sets two levels of performance – “Standard” and “Enhanced”. Commonly known as fire alarm cable.
BS 6004
Main standard for PVC wire and cable commonly used in final circuits in UK buildings, including the familiar "flat twin and earth" and "meter tails". Commonly known as PVC twin and earth, 6242Y, 6243Y.
BS 6004 (Table 6)
Arctic grade flexible cable previously in BS 7919 now in BS 6004. Commonly known as arctic grade.
BS 6231
Single core instrument wire commonly known as "tri-rated". Commonly known as panel wire, trirated.
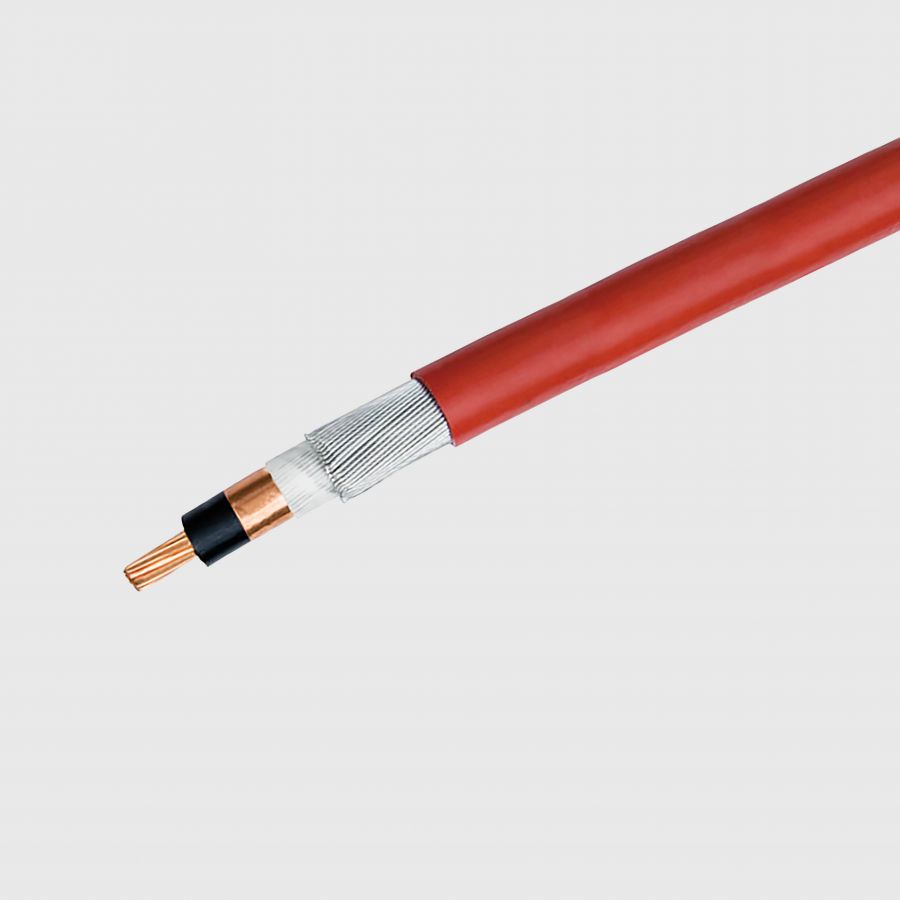

BS 6622
Armoured medium voltage cables with PVC sheathing, for rated voltages up to 33 kV. Commonly known as PVC sheathed MV.
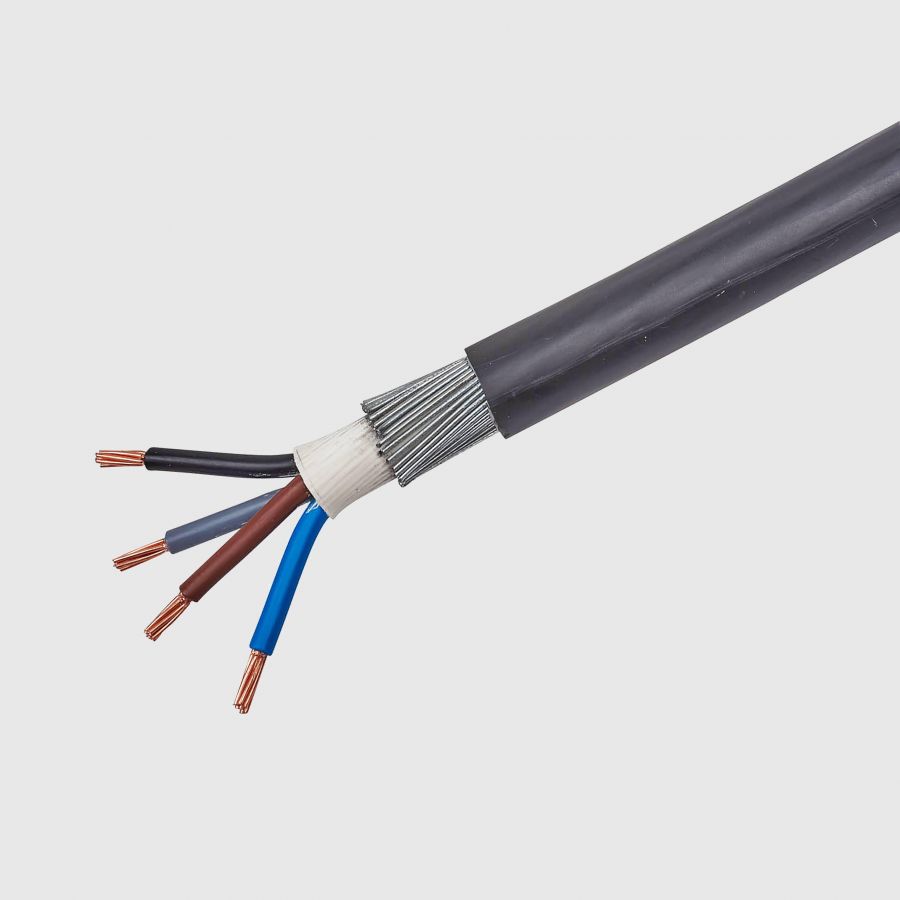

BS 6724
Armoured power cables with low smoke halogen free (LSHF) sheathing. Commonly known as low smoke sheathed armoured, SWA, AWA.
BS 7211
Low smoke halogen free (LSHF) versions of many of the types of wire and cable found in BS 6004. Commonly known as low smoke twin and earth, 6242B, 6243B.
BS 7629-1
British Standard type of “soft skin” fire resistant screened cables commonly used with fire alarms and emergency lighting. Commonly known as fire alarm / emergency lighting cable / soft skin fire alarm cable.
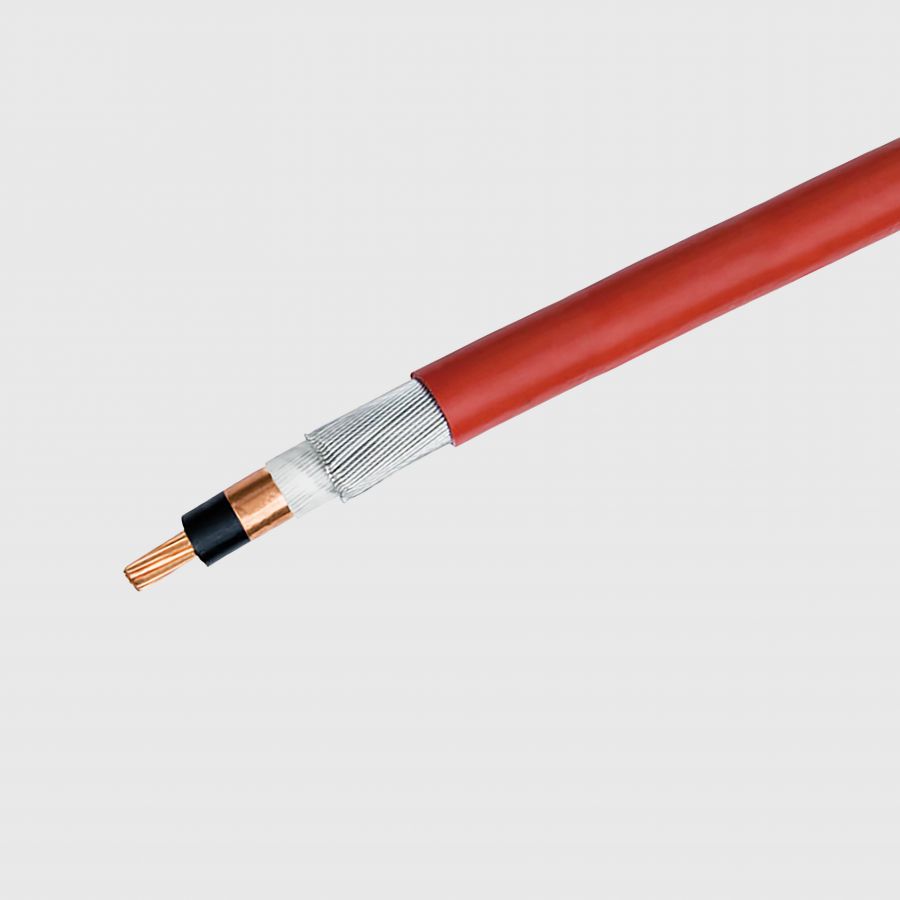

BS 7835
Armoured medium voltage cables with low smoke halogen free (LSHF) sheathing, for rated voltages up to 33 kV. Commonly known as low smoke sheathed MV.

BS 7846
Fire resisting armoured power cables with low smoke halogen free (LSHF) sheathing, and enhanced circuit integrity properties. Commonly known as fire resistant SWA, fire alarm / emergency lighting cable / soft skin fire alarm cable.

BS 7870 (many parts)
Low voltage and medium voltage polymeric insulated cables for use by distribution and generation utilities. Commonly known as utility MV / LV.

BS 7889
Non-armoured power cables with PVC sheathing. Commonly known as PVC sheathed unarmoured power.
BS 8436
Multi-core screened cables with low smoke halogen free (LSHF) sheathing for use in walls, partitions and building voids. Commonly known as nail proof.

BS 8573
Non-armoured power cables with low smoke halogen free (LSHF) sheathing. Commonly known as low smoke sheathed unarmoured power.
BS EN 50525 Series
Harmonised types of building wire, including “singles” and multicore cable with PVC or low smoke halogen free (LSHF) insulation/sheathing.
Data Cable
Screened and unscreened cable. Including category 5 - category 8, horizontal and work area cable testing to comply with ISO/IEC 11801, ANSI/TIA 568 and EN 50173 standards
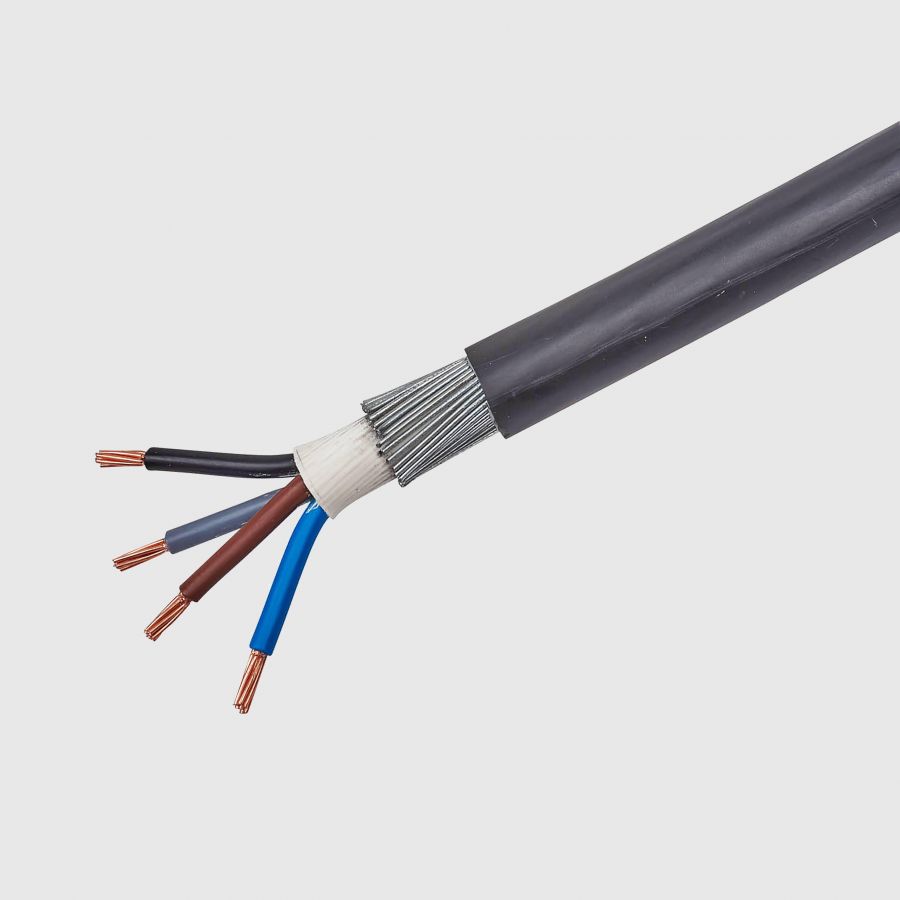

IEC 60502-1
Armoured and non-armoured low voltage power cables. Commonly known as IEC power / SWA.
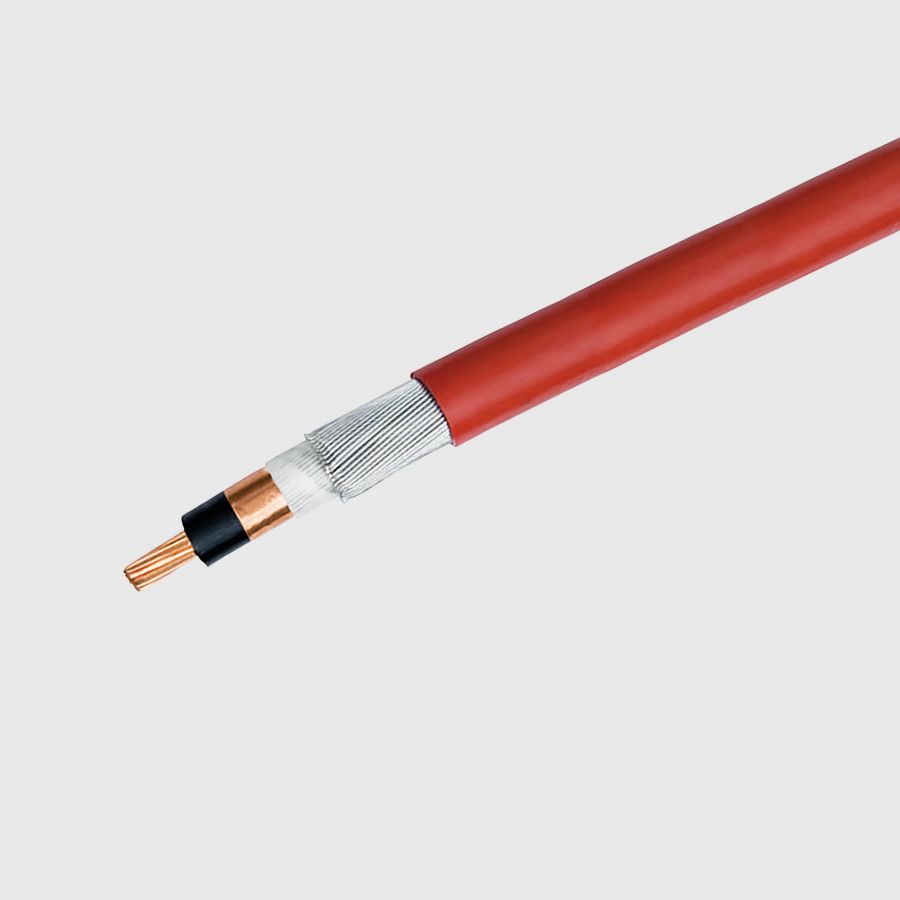

IEC 60502-2
Armoured and non-armoured medium voltage power cables with a variety of types of construction and materials, for rated voltages from 6 kV up to 36 kV.
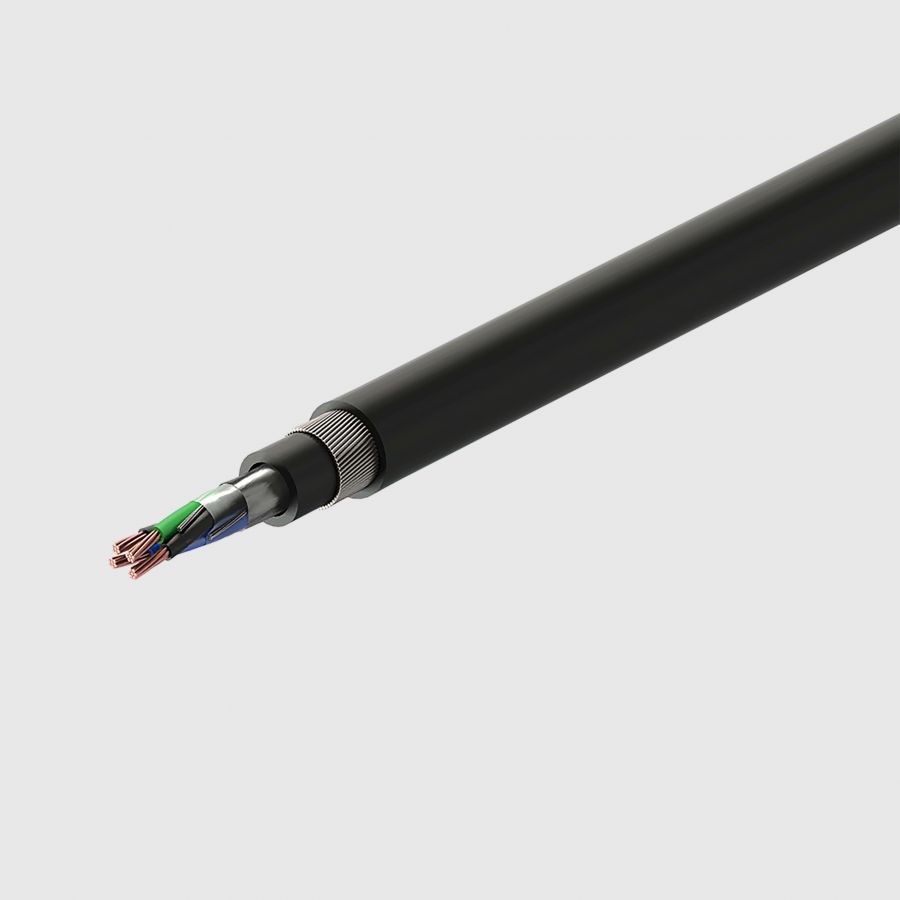

PAS 5308
Control and instrumentation cables. Commonly known as.
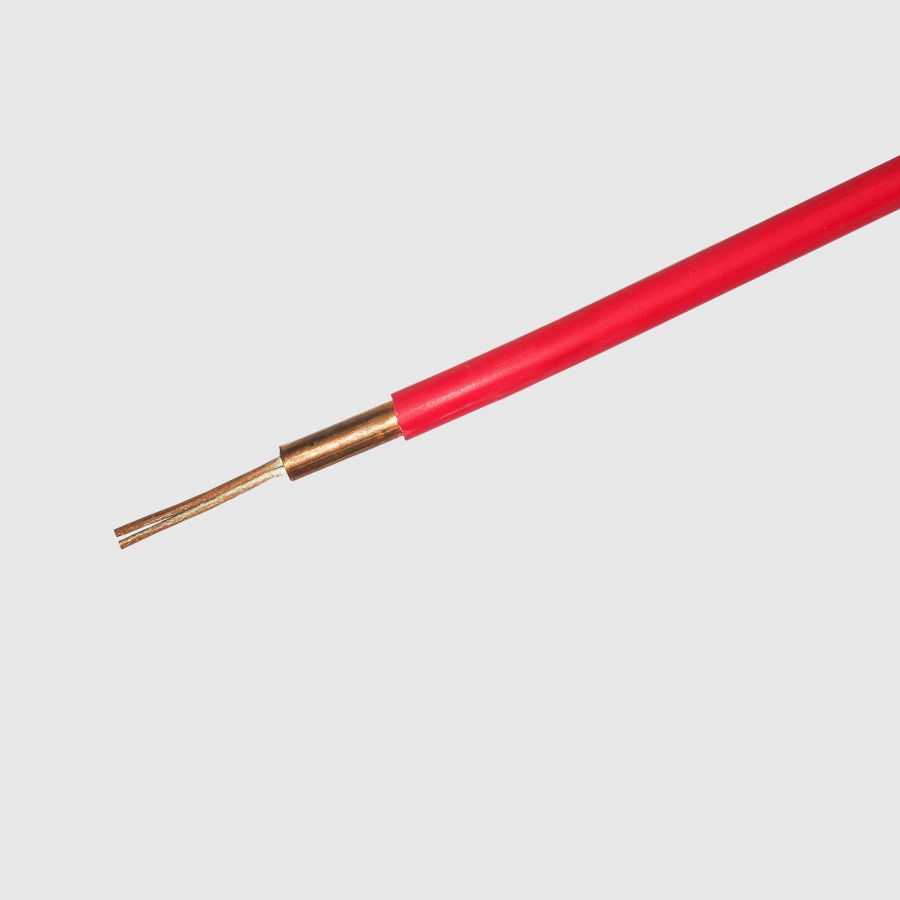

BS EN 60702-1
(IEC 60702-1) Mineral insulated cables. Commonly known as fire alarm / emergency lighting cable / soft skin fire alarm cable.




